Innovation Alphabet
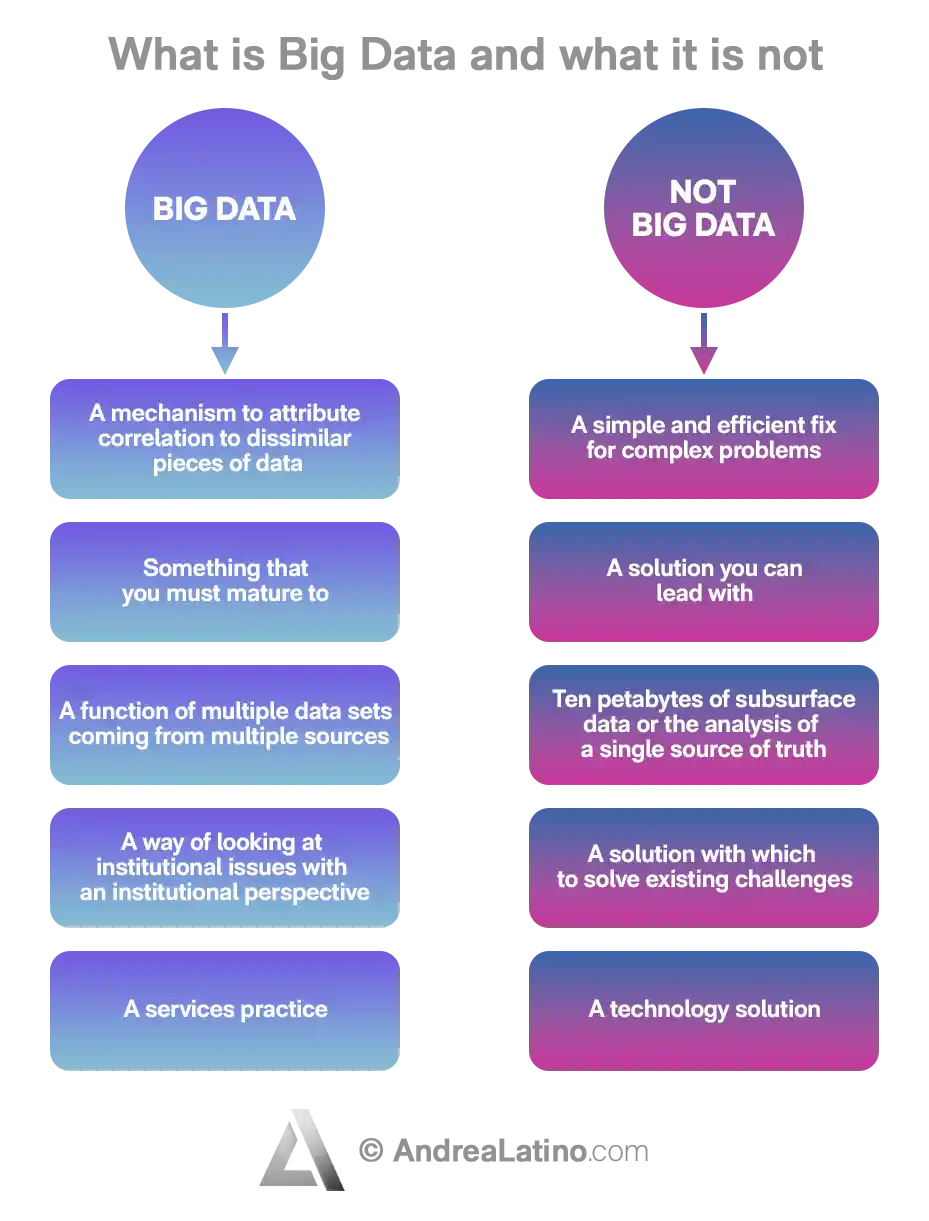
Big Data
In a nutshell
Any movement we make online generates a huge amount of information that will always be of interest to someone. The English term Big Data refers – literally – to the immense amount of data captured and managed every day by organizations and companies, stored and archived within specific systems. But, as is often the case, it is not so much the size that matters, but how it is used. That is, the ability to extract important insights from the data.


Application Fields
• Healthcare Industry: Within the health sector, the accumulation of Big Data enables research to improve increasingly personalized and effective drugs and treatments in response to existing diseases and conditions. The vast amount of data collected is analyzed through technologies aimed at extracting useful and coherent information from it. Data can bring innovation as much in the production and industrial component as in the research and development sector. But also in the purely clinical area of the healthcare field.
• Education: A load of information can paradoxically lighten the study load in education. Indeed, the collection of digital information can be leveraged to provide assistance in the evaluation of the performance of both teachers and students. As for the university world, research is currently being conducted to analyze through Big Data the dropout rates of students so as to understand the reasons for them. The aim is to reduce them, making university education meet the needs of young students.
• Tourism Industry: The tourism industry can benefit greatly from data analysis. Investing in in-depth knowledge of its customer base through the collection of information from loyalty programs certainly benefits the understanding of more frequent needs and issues expressed by travelers. As a consequence, it enables the development of more valued and tailored proposals and solutions.
Industries
• Big Data in the pharmaceutical industry
Chiesi, an Italian multinational pharmaceutical company based in Parma, is designing an architecture to manage information through Enterprise Intelligence. This business management approach applies new technologies and digital services paradigms within the company. The goal of the project is to improve customer engagement. Also, to integrate data across all collection channels through a comprehensive system that can manage the whole business activities.
• Big Data in the energy industry
Exploiting the combination of energy and Big Data, Eni has created a supercomputer capable of developing renewable energy. The object in question is a sealed floating hull composed of a pair of gyroscopic systems connected to as many generators. It converts sea wave energy into electricity through a mechanism activated by the oscillation produced by the sea. The computational capabilities offered by the supercomputer play an important role in aligning the operation of the gyroscopic system with local sea conditions. Indeed, we are talking about analyzing and cross-referencing large amounts of data from different sources. Those are meteorological data and information related to the actions of the machine. By integrating the adopted technologies with Big Data, it is possible to come up with response formulas suitable for each situation.

• Big Data in the service industry
Danske Bank has employed Big Data to improve fraud detection techniques. Investigations take place through machine learning algorithms integrated with analytics processes. Why? To probe tens of thousands of latent features and evaluate millions of online banking transactions in real time. The system returns information on real and fake fraudulent activity, enabling immediate response. Results: significant reduction in the cost of investigating false positives, 60% less fraud, $70 million operating profit. An increase in overall efficiency and considerable savings.
Do you have a Strategy & Innovation challenge to tackle? Let’s face it. Together.
C-levels from these companies (AND MORE) relied on my expertise to overcome thEIR CHALLENGES IN THIS AREA. And you can, too.
Can I help you?Business Functions
• Big Data in support of marketing
Amazon uses digital information in support of marketing activities to build recommendation systems that suggest the purchase of certain products based on each customer’s demonstrated interests. Amazon’s use of information is truly impressive in how multifaceted it is. We are talking about advance shipping models that send products to the closest warehouse to the selected user before they have even been purchased. Or, again, the optimization of prices on the web based on several parameters such as user activity or order history.
• Big Data in support of HR
Unilever had to ask for Big Data support within the HR department to resolve the corporate crisis that was triggered in 2017. It followed the lack of agreement with multinational Kraft Heinz, which had launched a takeover bid for the British company. Unilever’s HR team used data to analyze networks within the organization. In this way, they could identify the most appropriate way to reduce costs. The system was able to monitor employees’ moods and attitudes, allowing the company to record their reactions to defensive strategies and, as a result, decide which plan was the most appropriate to implement. The use of this information enabled the company to overcome the crisis and avert the need to divest the company.
• Big Data in support of management
United Overseas Bank (UOB) Limited decided to use data to improve the operation of its Risk Management. Risk Management is the business process aimed at comprehensive and integrated control of risks through systematic activities that are usually time-consuming. However, by resorting to data analytics, UOB is now able to complete the same process in a matter of minutes thanks to a high-performance solution that combines grid computing, matrix calculations and database analysis.
Stay in wonderland
Let me show you how deep the rabbit hole goes.
Check out more of the Innovation Alphabet:

3D Printing
3D Printing
“3D printing” is a process carried out by an electronic device which, instead of resorting to the canonical ink, it molds almost any kind of material: from concrete to living tissue, most usually plastic, but also metal. And the operating principle is similar to that of a traditional printer. The creation of three-dimensional models can lead to the redesign of a company’s production capabilities.
Dive In
5G
5G
5G is the new frontier of cellular telephony. It was designed to improve (or completely replace) previous generations of mobile networks. The 5th generation features lower latency, ensuring flawless performance of business applications and many other digital experiences – thus enabling the new cultural generations to furiously play Fortnite away from home.
Dive In
Advanced Analytics
Advanced Analytics
The term “Advanced Analytics” refers to the ability to autonomously or semi-autonomously analyze data and content to identify correlations, develop analyses, predictions, and recommendations. It is not just a matter of collecting information and then organizing it into watertight compartments: the ultimate goal is to identify a dialogue pattern from a data-driven perspective.
Dive In
Agile
Agile
Agile is an approach to software development designed to respond to change. Teams quickly analyze the context in which they operate, identify uncertainties faced, and figure out how to adapt to always move forward. Interaction between individuals comes before processes and tools; collaboration with the customer is more important than negotiating contracts.
Dive In
Ansoff Matrix
Ansoff Matrix
The Ansoff Matrix is a marketing planning model that arises from the intersection of new and existing products and markets. It derives four possible strategies for expanding the company’s market, which are built around four variables with a changeable factor of risks and possibilities: existing product, new product, existing market, new market.
Dive In
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence is not strictly defined. Basically, it is a computer system able to make decisions in an independent and flexible way. A good AI application can perform everyday tasks better than an average person (e.g., identifying other people from their photos on social media or beating the best chess player). Nothing to fear, then. Unless you are a chess champion.
Dive In
Artificial Scarcity
Artificial Scarcity
We often tend to desire what we cannot have. Or what we are in danger of losing: Artificial Scarcity is a strategy that flaunts a limited number of items that do not correspond to actual availability. The goal is to stimulate the perception in consumers that the stock of items is about to run out and thus create a need based on the “fear of being cut off” or the intention to buy the item in order to resell it at a higher price.
Dive In
Attack Surface
Attack Surface
The term attack surface refers to the part of a system that may be subject to attack or breach by hackers. The smaller that surface is, the easier it will be to protect it. Indeed, the Internet is an ocean of deep, dark waters: those who navigate it must be aware that they are exposing themselves to a flood of digital risks. Yet, ironically, we do not need a big boat to shelter us.
Dive In
Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality is an ever-evolving technology that overlays multimedia information on top of our common sensory horizon to gain a deeper understanding of our surroundings. No, it doesn’t allow you to step out of the Matrix dream simulation, nor can it be accessed by swallowing a red pill. But neither is it the disturbing experience of the Playtest episode of Black Mirror.
Dive In
Balanced Scorecard
Balanced Scorecard
In business, as in life, you need balance. The Balanced Scorecard is a holistic tool for strategic management. It offers, in fact, the possibility of assessing corporate performance in its wholeness. An overview that embraces four perspectives: the business/financial side, customers and stakeholders, internal processes, and learning and growth.
Dive In