Innovation Alphabet
Computer Vision
In a nutshell
Computer vision (or “artificial vision”) is an area of computer science that attempts to replicate the operation of human vision on electronic devices so that they can take actions or formulate responses based on information gleaned from digital images, videos, and other visual input. As such, it is one of the most compelling and interesting challenges in artificial intelligence.


If human sight is an extremely complex sense itself, how could an attempt to endow machines with the same sensitivity not be so? The key difference is that we humans recognize objects not only by experience, but also by the context in which they are found. That’s an extremely more complicated ability for a technological device to learn.
Application Fields
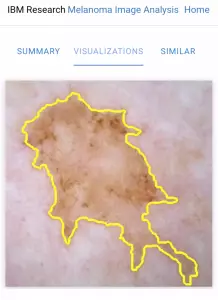
• Healthcare: Computer vision serves as an aid in diagnosing diseases such as breast and skin cancer. This allows doctors to detect differences between cancerous and non-cancerous images. In addition, computer vision can be used to classify cells and identify disease early. And, again, other applications of computer vision can detect neurological and musculoskeletal diseases such as, for example, a stroke.
• Transportation: In the transportation sector, a technological vision is applied for automatic vehicle classification. It enables detection of traffic violations through monitoring systems and cameras, traffic analysis, or parking occupancy control by reporting vacant and occupied spaces.
• Retail: Computer vision technologies are capable of counting and keeping an eye on customers entering a store, as well as collecting data (through deep learning) about the departments of the store most frequented by customers. Machine vision is also able to analyze waiting times in stores so that customers know how long they will have to spend in line.

Industries
• Computer Vision in the transportation industry
With the rapid growth of affordable sensors such as closed-circuit television (CCTV) cameras, Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR), and thermal imaging devices, vehicles can be detected, tracked, and classified as they flow over multiple lanes simultaneously. The accuracy of vehicle classification can be optimized through the combination of the sensors mentioned above.
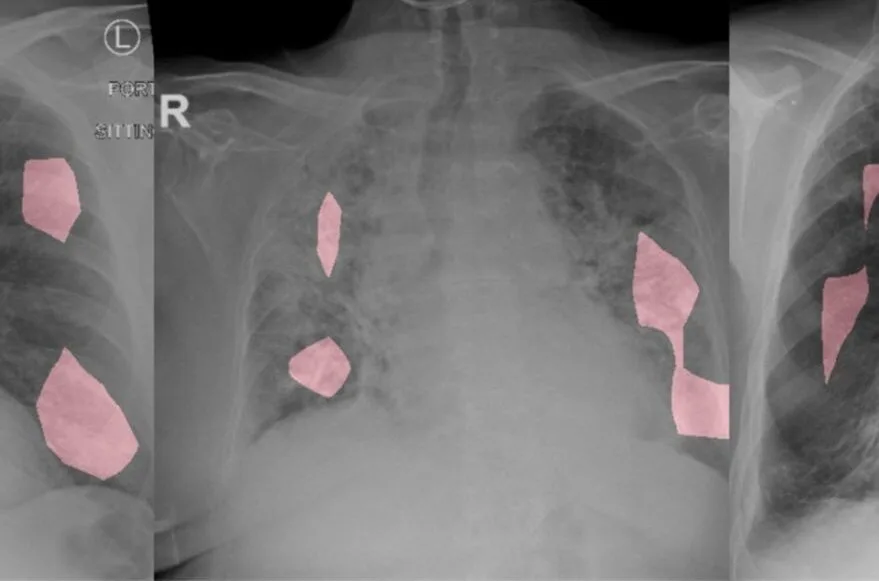
• Computer Vision in the healthcare industry
There are several computer vision models for X-ray-based diagnosis of Covid-19. The most famous is COVID-Net, a system that detects virus-positive cases by chest X-ray (CXR) developed by the Canadian company DarwinAI.
• Computer Vision in the sports industry
ScoringNet is a three-dimensional CNN network architecture that automatically monitors the scoring of athletes in sports activities such as swimming or figure skating.
Do you have a Strategy & Innovation challenge to tackle? Let’s face it. Together.
C-levels from these companies (AND MORE) relied on my expertise to overcome thEIR CHALLENGES IN THIS AREA. And you can, too.
Can I help you?Business Functions
• Computer Vision in support of quality control
Ivisys is a company building 2D and 3D inspection solutions. They use a tool called ShapeInspector. As the name suggests, it moves the product that needs to be verified into the system and then runs the inspection sequence with optimized light and camera position. The results of these inspections can be quickly verified and stored in the system’s internal database. Then someone will replace the product with the next one. All humans have to do is select a product recipe for the inspection, since even the product can be loaded by the robot.
• Computer Vision in support of customer care
Customer service is shifting more and more toward visual communication thanks to the increasing popularity of video chat technologies and video tutorials. Hence, CV can add key data to customers’ profiles based on visual information such as facial profile, home environment, purchased devices, and so on. Take, for example, a customer who calls to report trouble with his coffee machine. He’ll just have to upload images of his machine and image recognition will do the rest. The model is identified and common issues are suggested. The call is classified and routed to an agent for prompt service.
• Computer Vision in support of safety
Machines can track objects in a video and detect them in an image. This allows companies to enhance their security significantly. How? Well, visual data from security cameras, for example, can be combined with other data types, such as data from motion or IR sensors. As a consequence, the AI system can detect and track suspicious items or people moving within a specific location. Moreover, pattern recognition algorithms can flag violations of adequate dress codes for dangerous production.
Stay in wonderland
Let me show you how deep the rabbit hole goes.
Check out more of the Innovation Alphabet:

3D Printing
3D Printing
“3D printing” is a process carried out by an electronic device which, instead of resorting to the canonical ink, it molds almost any kind of material: from concrete to living tissue, most usually plastic, but also metal. And the operating principle is similar to that of a traditional printer. The creation of three-dimensional models can lead to the redesign of a company’s production capabilities.
Dive In
5G
5G
5G is the new frontier of cellular telephony. It was designed to improve (or completely replace) previous generations of mobile networks. The 5th generation features lower latency, ensuring flawless performance of business applications and many other digital experiences – thus enabling the new cultural generations to furiously play Fortnite away from home.
Dive In
Advanced Analytics
Advanced Analytics
The term “Advanced Analytics” refers to the ability to autonomously or semi-autonomously analyze data and content to identify correlations, develop analyses, predictions, and recommendations. It is not just a matter of collecting information and then organizing it into watertight compartments: the ultimate goal is to identify a dialogue pattern from a data-driven perspective.
Dive In
Agile
Agile
Agile is an approach to software development designed to respond to change. Teams quickly analyze the context in which they operate, identify uncertainties faced, and figure out how to adapt to always move forward. Interaction between individuals comes before processes and tools; collaboration with the customer is more important than negotiating contracts.
Dive In
Ansoff Matrix
Ansoff Matrix
The Ansoff Matrix is a marketing planning model that arises from the intersection of new and existing products and markets. It derives four possible strategies for expanding the company’s market, which are built around four variables with a changeable factor of risks and possibilities: existing product, new product, existing market, new market.
Dive In
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence is not strictly defined. Basically, it is a computer system able to make decisions in an independent and flexible way. A good AI application can perform everyday tasks better than an average person (e.g., identifying other people from their photos on social media or beating the best chess player). Nothing to fear, then. Unless you are a chess champion.
Dive In
Artificial Scarcity
Artificial Scarcity
We often tend to desire what we cannot have. Or what we are in danger of losing: Artificial Scarcity is a strategy that flaunts a limited number of items that do not correspond to actual availability. The goal is to stimulate the perception in consumers that the stock of items is about to run out and thus create a need based on the “fear of being cut off” or the intention to buy the item in order to resell it at a higher price.
Dive In
Attack Surface
Attack Surface
The term attack surface refers to the part of a system that may be subject to attack or breach by hackers. The smaller that surface is, the easier it will be to protect it. Indeed, the Internet is an ocean of deep, dark waters: those who navigate it must be aware that they are exposing themselves to a flood of digital risks. Yet, ironically, we do not need a big boat to shelter us.
Dive In
Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality is an ever-evolving technology that overlays multimedia information on top of our common sensory horizon to gain a deeper understanding of our surroundings. No, it doesn’t allow you to step out of the Matrix dream simulation, nor can it be accessed by swallowing a red pill. But neither is it the disturbing experience of the Playtest episode of Black Mirror.
Dive In
Balanced Scorecard
Balanced Scorecard
In business, as in life, you need balance. The Balanced Scorecard is a holistic tool for strategic management. It offers, in fact, the possibility of assessing corporate performance in its wholeness. An overview that embraces four perspectives: the business/financial side, customers and stakeholders, internal processes, and learning and growth.
Dive In