Innovation Alphabet
Quantitative Strategic Planning Matrix (QSPM)
in a nutshell
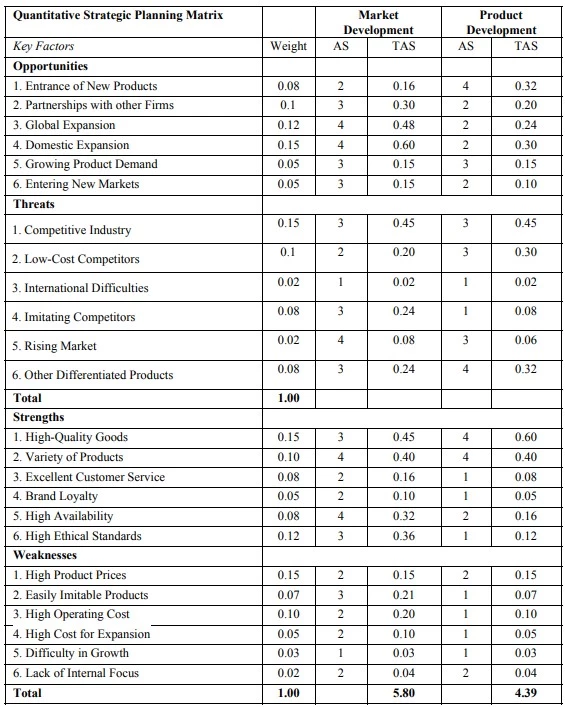
Quantitative Strategic Planning Matrix (QSPM) is a management tool that provides an analytical method for objectively evaluating the most suitable strategy among the list of alternatives. The Matrix is based on the collection of data and the use of quantitative factors for strategic planning so as to minimize the subjective and intuitive input of business managers.


Steps
1) Start with the IFE & EFE Matrices to derive internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats, respectively. Then place the data obtained in the left column of the QSPM.
2) Just as with the IFE & EFE matrices, assign a weight to each factor and place them in the first right column.
3) Review the developed matrices, and identify some alternative strategies, which will be further evaluated. The alternative strategies are reported in the top row of the matrix, possibly grouping them in mutually exclusive clusters.
4) Now determine the attractiveness scores (AS) for each factor and each possible strategy from the following question: “Does it make a difference in deciding which strategy to pursue?” If the answer is yes, the attributable values range from 1 to 4 in ascending order of attractiveness.
5) Calculate the Total Attractiveness Score (TAS), which is the product of multiplying the weights by the attractiveness scores. The TAS indicates the relative attractiveness of each key factor and its individual strategy. The higher the score, the higher the interest in the strategic alternative.
6) Finally, the total sum of attractiveness is quantified by adding up all the Total Attractiveness Scores in each column of the QSPM. This is the crucial step. The highest score will reveal the most attractive strategy among the proposed alternatives.
Do you have a Strategy & Innovation challenge to tackle? Let’s face it. Together.
C-levels from these companies (AND MORE) relied on my expertise to overcome thEIR CHALLENGES IN THIS AREA. And You can, too.
Can I help you?Application Fields
• Decision-making: In the process leading to the development of an effective strategy for a company, the clearest possible objective consideration of internal and external factors proves to be crucial, as it enables a complete and comprehensive picture to be drawn. In this way, the strategy that ultimately turns out to be successful will be so with merit.
• Strategy: A support against indecision, impulse, and subjectivity. As the name of the Matrix suggests, this tool is essential for selecting a strategy that can help a business grow in its industry. But first it is necessary to have in mind the general state and context in which one has decided to land.
• Transversality: The QSPM is not only applicable by large companies, but also and especially for SMEs or nonprofit organizations. Implementing an effective strategy, after all, must be the goal of any business, regardless of size or ambition.
Industries
• QSPM in the retail industry
A hypothetical Quantitative Strategic Planning Matrix applied to Starbucks could reveal some key aspects to be improved. For example, considering internal and external factors, the company would do better to reduce costs and try to distinguish itself from competitors. Or, again, Starbucks might consider conceiving a beverage never tasted before.
• QSPM in the E-commerce industry
Analyzing Amazon through a QSP Matrix could point to a possible strategy of approaching the Asian market. Here, the direct competitor Alibaba is very present. Consequently, the study and identification of Chinese e-commerce weaknesses could point the Silk Road to the American giant.
• QSPM in the IT industry
BaridSoft Company is a company that offers products related to the IT sector, and especially in the field of Office Automation. A QSPM analysis conducted by the International Journal of Scientific Management and Development revealed how the joint analysis of internal and external factors can lead to gathering key opportunities for solving critical contexts.
Stay in wonderland
Let me show you how deep the rabbit hole goes.
Check out more of the Innovation Alphabet:

3D Printing
3D Printing
“3D printing” is a process carried out by an electronic device which, instead of resorting to the canonical ink, it molds almost any kind of material: from concrete to living tissue, most usually plastic, but also metal. And the operating principle is similar to that of a traditional printer. The creation of three-dimensional models can lead to the redesign of a company’s production capabilities.
Dive In
5G
5G
5G is the new frontier of cellular telephony. It was designed to improve (or completely replace) previous generations of mobile networks. The 5th generation features lower latency, ensuring flawless performance of business applications and many other digital experiences – thus enabling the new cultural generations to furiously play Fortnite away from home.
Dive In
Advanced Analytics
Advanced Analytics
The term “Advanced Analytics” refers to the ability to autonomously or semi-autonomously analyze data and content to identify correlations, develop analyses, predictions, and recommendations. It is not just a matter of collecting information and then organizing it into watertight compartments: the ultimate goal is to identify a dialogue pattern from a data-driven perspective.
Dive In
Agile
Agile
Agile is an approach to software development designed to respond to change. Teams quickly analyze the context in which they operate, identify uncertainties faced, and figure out how to adapt to always move forward. Interaction between individuals comes before processes and tools; collaboration with the customer is more important than negotiating contracts.
Dive In
Ansoff Matrix
Ansoff Matrix
The Ansoff Matrix is a marketing planning model that arises from the intersection of new and existing products and markets. It derives four possible strategies for expanding the company’s market, which are built around four variables with a changeable factor of risks and possibilities: existing product, new product, existing market, new market.
Dive In
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence is not strictly defined. Basically, it is a computer system able to make decisions in an independent and flexible way. A good AI application can perform everyday tasks better than an average person (e.g., identifying other people from their photos on social media or beating the best chess player). Nothing to fear, then. Unless you are a chess champion.
Dive In
Artificial Scarcity
Artificial Scarcity
We often tend to desire what we cannot have. Or what we are in danger of losing: Artificial Scarcity is a strategy that flaunts a limited number of items that do not correspond to actual availability. The goal is to stimulate the perception in consumers that the stock of items is about to run out and thus create a need based on the “fear of being cut off” or the intention to buy the item in order to resell it at a higher price.
Dive In
Attack Surface
Attack Surface
The term attack surface refers to the part of a system that may be subject to attack or breach by hackers. The smaller that surface is, the easier it will be to protect it. Indeed, the Internet is an ocean of deep, dark waters: those who navigate it must be aware that they are exposing themselves to a flood of digital risks. Yet, ironically, we do not need a big boat to shelter us.
Dive In
Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality is an ever-evolving technology that overlays multimedia information on top of our common sensory horizon to gain a deeper understanding of our surroundings. No, it doesn’t allow you to step out of the Matrix dream simulation, nor can it be accessed by swallowing a red pill. But neither is it the disturbing experience of the Playtest episode of Black Mirror.
Dive In
Balanced Scorecard
Balanced Scorecard
In business, as in life, you need balance. The Balanced Scorecard is a holistic tool for strategic management. It offers, in fact, the possibility of assessing corporate performance in its wholeness. An overview that embraces four perspectives: the business/financial side, customers and stakeholders, internal processes, and learning and growth.
Dive In