Innovation Alphabet
Bowman’s Strategy Clock
in a nutshell
Speaking of clocks, it’s time to analyze a company’s competitive position in relation to competitors’ offerings. Bowman’s Strategy Clock is a model for mapping product positions in the marketplace according to price and perceived value. The “hands” of the clock identify 8 positions, each relating to a different approach aimed at business success.


BOWMAN’S DIALS
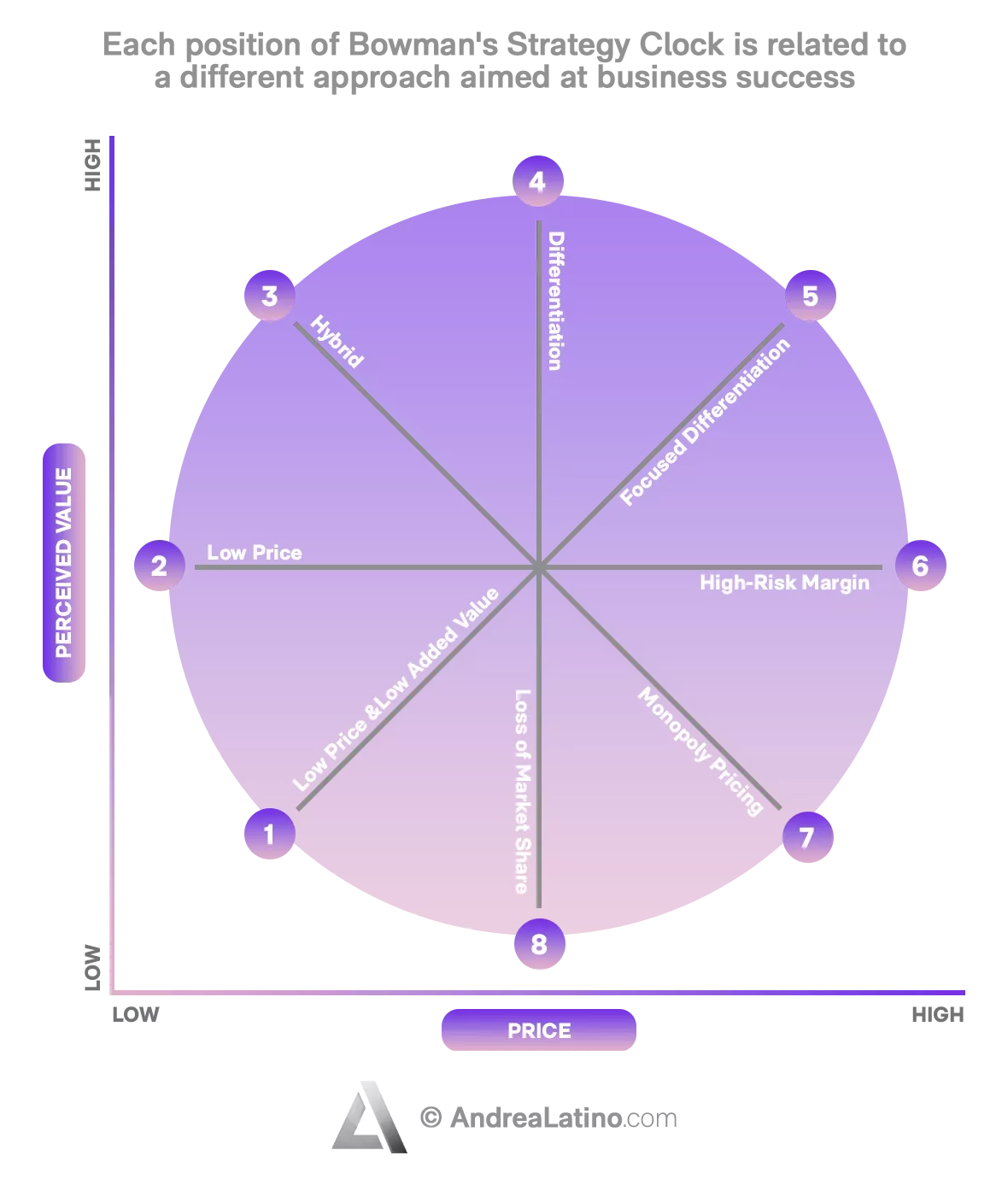
Low Price and Low Added Value: This is the least competitive strategic position, focused on sales volume. The product lacks differentiated value, but the prices are so low that they are attractive to consumers at least once.
Low Price: Companies in this category are the low-cost leaders: they drive prices to the bare minimum but balance poor margins with very high volume. It is important that the company has sufficiently large volumes or strong strategic reasons, otherwise it risks triggering a price war that only benefits consumers.
Hybrid (Moderate Price/Moderate Differentiation): In this position, companies sell products or services at low cost, offering a form of differentiation. That is, the value perceived by customers is higher than that of competing offerings.
Differentiation: By differentiating a product or service, a unique value is perceived. The company strives to distinguish itself from rivals through a branding strategy that ensures it becomes synonymous with quality as well as price.
Focused Differentiation: This pertains to high-end products. The prices may be high, but the perceived value is, correspondingly, much higher. These are products that usually target a niche market (focused, indeed), willing to pay a much higher price premium than the actual value. A strategy that can produce significant profits but is difficult to sustain.
High-Risk Margin: As the name suggests, this is the riskiest strategy, so the company should be aware of alternatives before embarking on this path. It consists of selling a standard product at a higher price without a corresponding increase in value. It is a short-term strategy, since in a competitive market an unjustified overprice is soon discovered.
Monopoly Pricing: A single company controls a product or service and its prices in the market. Consequently, the business that enjoys such positioning should not worry about perceived value or cost. In general, however, institutional bodies promote a market of fair competition, and sooner or later all monopolies come to an end. Therefore, it is good for the business to continue to monitor external variables.
Loss of Market Share: This is the most dangerous position. Loss of market share is typical of a firm in decline or moving away from the market itself. The products are of inferior quality, but the price matches the value proposition of a superior competitor. It is a tactic that, in the long run, will alienate customers.
Application Fields
• Marketing: One of the most important phases of the customer journey is the final one: the advocacy phase, when the customer manifests an emotional relationship with the brand and is a self-appointed spokesperson. In order for the consumer journey to reach a happy ending, it would certainly be profitable for a company to implement marketing strategies that expand the perceived value of the product or service offered.
• New product design: Through an effective study of the market and customer needs, a company can think about introducing new products that can be given very high value. After all, a diverse range of goods and services can only make a company more attractive and more organized to respond promptly to needs that might arise with value propositions.
• Antitrust: Paying attention to domestic and especially international regulations is crucial for any business. Consequently, you should weigh your strategy and not cheat on pricing in a way that could result in unfair competition.
Do you have a Strategy & Innovation challenge to tackle? Let’s face it. Together.
C-levels from these companies (AND MORE) relied on my expertise to overcome thEIR CHALLENGES IN THIS AREA. And you can, too.
Can I help you?Industries
• Bowman’s Strategy Clock in the retail industry
Dollar Tree Stores is an American discount chain operating in more than 40 states. It sells most products for as little as a dollar, particularly party items. These are products, therefore, that are thrown away immediately after use. It is a clear example of the Low Price and Low Value Added strategy.
• Bowman’s Strategy Clock in the aviation industry
Wizz Air is a Hungarian low-cost airline founded in 2004. Today it travels to 44 countries. Wizz Air has been able to deploy an effective Low Price strategy, as flights cost significantly less than even the cheapest competitors.
• Bowman’s Strategy Clock in the technology industry
During the 1990s, Microsoft found itself in a monopoly position: it was, in fact, the only reliable company selling computers and operating systems. So, it decided to exploit the situation and price its products far too high. And it paid dearly for it, as the European Union slapped Microsoft with a fine of $1.3 billion.
Business Functions
• Bowman’s Strategy Clock in support of branding
To stay on topic, Rolex is the Swiss company specialized in making luxury wristwatches. Like other fine goods companies, product quality and image are the real pillars of success. It is the tactic of Focused Differentiation: the perception of value is enough to justify high prices.
• Bowman’s Strategy Clock in support of core value
If you have ever passed within a few miles of a Lush store, you may have caught a whiff of it. The famous American skincare brand has been able to differentiate itself from competitors by adopting a hybrid strategy that leveraged the company’s ethical and sustainable values as a form of differentiation. High value at competitive prices.
• Bowman’s Strategy Clock in support of storytelling
LVMH is the multinational corporation under whose umbrella different realities shelter themselves: from Louis Vuitton to Dior, from Moët to Sephora. The luxury brands that, in fact, contribute to the group’s success sell products with high profit margins, guaranteed by a disproportionate perception of value. It is also due, in part, to the storytelling promoted by the companies. It is another marketing strategy concerning the fifth hand on Bowman’s clock.
Stay in wonderland
Let me show you how deep the rabbit hole goes.
Check out more of the Innovation Alphabet:

3D Printing
3D Printing
“3D printing” is a process carried out by an electronic device which, instead of resorting to the canonical ink, it molds almost any kind of material: from concrete to living tissue, most usually plastic, but also metal. And the operating principle is similar to that of a traditional printer. The creation of three-dimensional models can lead to the redesign of a company’s production capabilities.
Dive In
5G
5G
5G is the new frontier of cellular telephony. It was designed to improve (or completely replace) previous generations of mobile networks. The 5th generation features lower latency, ensuring flawless performance of business applications and many other digital experiences – thus enabling the new cultural generations to furiously play Fortnite away from home.
Dive In
Advanced Analytics
Advanced Analytics
The term “Advanced Analytics” refers to the ability to autonomously or semi-autonomously analyze data and content to identify correlations, develop analyses, predictions, and recommendations. It is not just a matter of collecting information and then organizing it into watertight compartments: the ultimate goal is to identify a dialogue pattern from a data-driven perspective.
Dive In
Agile
Agile
Agile is an approach to software development designed to respond to change. Teams quickly analyze the context in which they operate, identify uncertainties faced, and figure out how to adapt to always move forward. Interaction between individuals comes before processes and tools; collaboration with the customer is more important than negotiating contracts.
Dive In
Ansoff Matrix
Ansoff Matrix
The Ansoff Matrix is a marketing planning model that arises from the intersection of new and existing products and markets. It derives four possible strategies for expanding the company’s market, which are built around four variables with a changeable factor of risks and possibilities: existing product, new product, existing market, new market.
Dive In
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence is not strictly defined. Basically, it is a computer system able to make decisions in an independent and flexible way. A good AI application can perform everyday tasks better than an average person (e.g., identifying other people from their photos on social media or beating the best chess player). Nothing to fear, then. Unless you are a chess champion.
Dive In
Artificial Scarcity
Artificial Scarcity
We often tend to desire what we cannot have. Or what we are in danger of losing: Artificial Scarcity is a strategy that flaunts a limited number of items that do not correspond to actual availability. The goal is to stimulate the perception in consumers that the stock of items is about to run out and thus create a need based on the “fear of being cut off” or the intention to buy the item in order to resell it at a higher price.
Dive In
Attack Surface
Attack Surface
The term attack surface refers to the part of a system that may be subject to attack or breach by hackers. The smaller that surface is, the easier it will be to protect it. Indeed, the Internet is an ocean of deep, dark waters: those who navigate it must be aware that they are exposing themselves to a flood of digital risks. Yet, ironically, we do not need a big boat to shelter us.
Dive In
Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality is an ever-evolving technology that overlays multimedia information on top of our common sensory horizon to gain a deeper understanding of our surroundings. No, it doesn’t allow you to step out of the Matrix dream simulation, nor can it be accessed by swallowing a red pill. But neither is it the disturbing experience of the Playtest episode of Black Mirror.
Dive In
Balanced Scorecard
Balanced Scorecard
In business, as in life, you need balance. The Balanced Scorecard is a holistic tool for strategic management. It offers, in fact, the possibility of assessing corporate performance in its wholeness. An overview that embraces four perspectives: the business/financial side, customers and stakeholders, internal processes, and learning and growth.
Dive In