Innovation Alphabet
Customer Journey
In a nutshell
Customer Journey refers to the path taken by consumers in discovering a brand or service through a series of touchpoints that can influence their purchasing decision-making process. In short, the consumer journey is not a Jules Verne novel, but a valuable tool for improving customer acquisition and retention strategies.
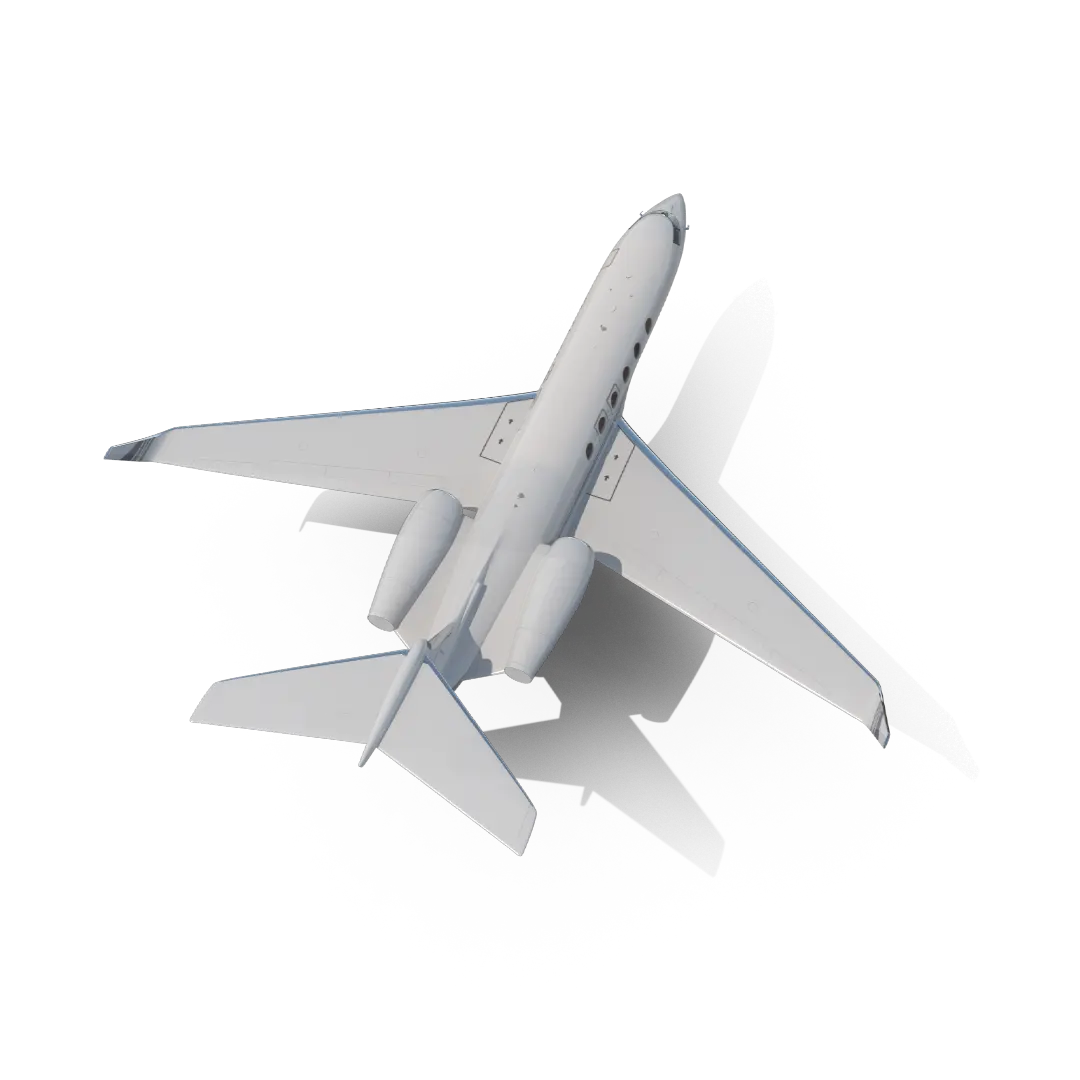


Customer Journey phases
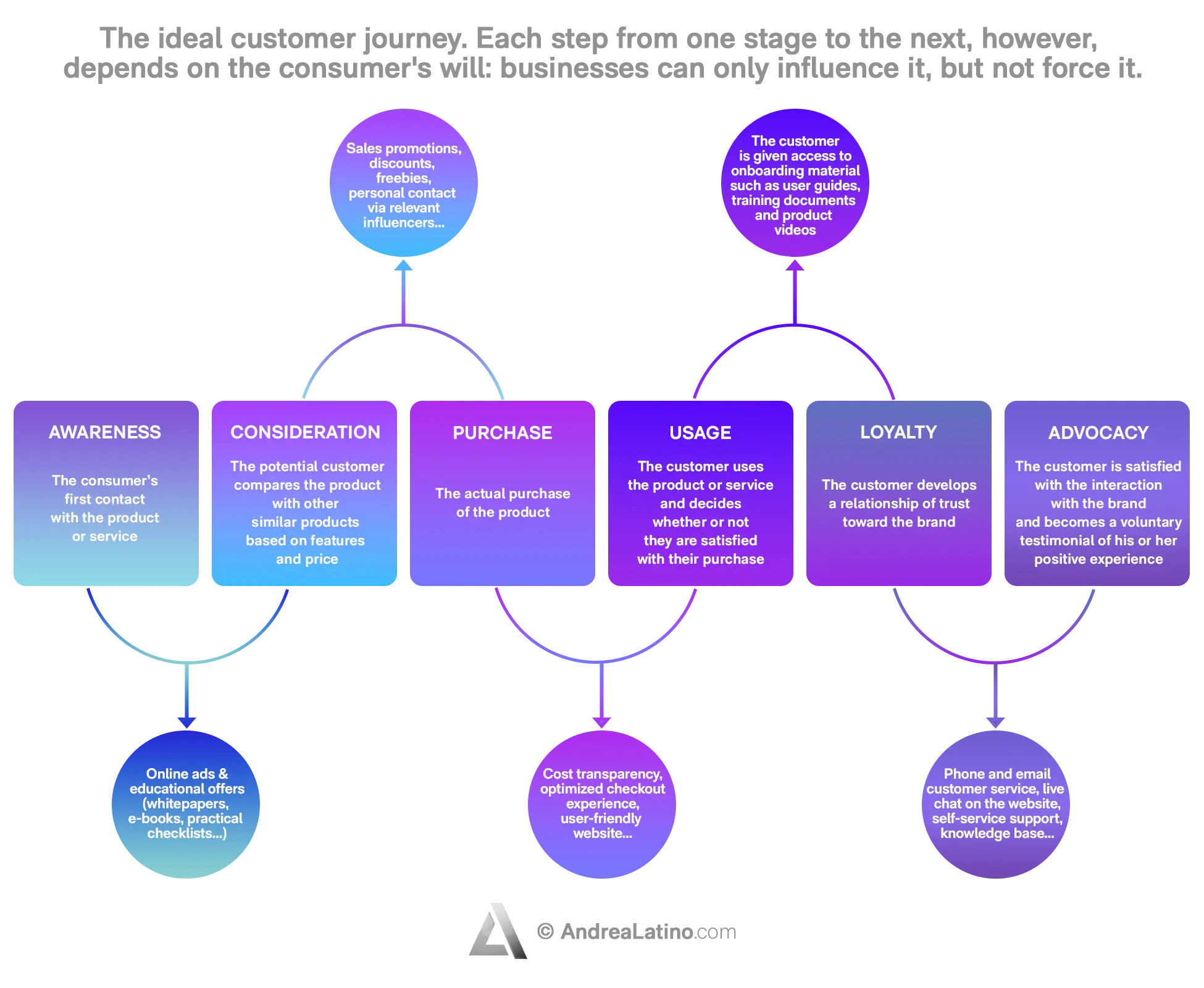
Customer Journey vs Digital Strategy
First of all, it is worth making one thing clear: customer journey is not a fixed and obligatory path. It is correct to try to map the customer journey, but users will always be free to move as they wish. Hence, customer journey is the most accurate approximation possible of the behavior we think the user will have.
A digital strategy, on the other hand, concerns all those measures we implement to try to get users to take certain actions and thus move them from one stage of the customer journey to another. This means that digital strategy is chosen by the company, but it only has the power to influence the consumer.
For example, if the user is in the “Consideration” stage, the company might try to move them to the next stage through a tactical activation with a 20 percent discount. If the user responds positively to this action, they will move on to “Purchase”. But if they don’t respond, at least the company has done its best.
Customer Journey Ideal Steps
Ideally, the journey originates from a consumer need and ends with the purchase of a good or service. The customer journey can be broken down into 6 important successive stages:
1. Awareness: The consumer’s first contact with the product or service.
2. Consideration: The potential customer compares the product with other similar products based on features and price.
3. Purchase: The actual purchase of the product.
4. Usage: The customer uses the product or service and decides whether or not they are satisfied with their purchase.
5. Loyalty: The customer develops a relationship of trust toward the brand.
6. Advocacy: The customer, satisfied with the interaction with the brand, becomes a voluntary testimonial of his or her positive experience.
Application fields
• Marketing: The customer journey is a marketing model that enables companies to understand and improve the overall consumer experience and perceived competitive advantage.
• Advertising: One of the touchpoints through which the potential consumer comes into contact with the product. A good advertising campaign becomes the gateway to a large number of trips.
• CRM (Customer Relationship Management). CRM strategies accompany the consumer journey to obtain information regarding potential customers’ preferences and consequently increase purchase frequency.
Do you have a Marketing & Sales challenge to tackle? Let’s face it. Together.
C-levels from these companies (AND MORE) relied on my expertise to overcome thEIR CHALLENGES IN THIS AREA. And You can, too.
Can I help you?Industries
• Customer Journey in CRM software
All Apple users have an Apple ID, a profile that allows access to the various services offered by the brand. The account contains all personal information about the user: the music he or she listens to, the books he or she reads, the apps he or she downloads, and so on. For the company, it is a way to collect and keep up-to-date data on customers, offering them services in line with their preferences and needs.
• Customer Journey in marketing automation
Opsview is a software company that offers management and monitoring services for IT infrastructure. The original goal was to distinguish two types of leads (potential buyers): those who were already satisfied and those who might be interested in purchasing more content. Opsview resorted to marketing automation to classify leads from the “website” touchpoint by subjecting users to a questionnaire and scoring them according to their responses. Needless to say, this enabled the company to increase customers and consequently revenue.
Business Functions
• Customer Journey in support of website performance monitoring
Google Analytics is a free platform that allows you to monitor the performance of a website or application. It tracks and records web traffic by providing comprehensive statistics on the previous path of visitors and their interaction patterns. The platform then allows the characteristics of the site’s target “audience” to be drawn up based on customized metrics. The collected data can implement advertising, social and digital PR campaigns, as well as to measure the ROI (Return on Investment) of activated web marketing campaigns.
• Customer Journey in support of advertising
Another software that fits into the consumer’s path is Google Ads. It allows advertising space to be placed within Google’s search pages. The ads are displayed above or below the search results and are selected by an algorithm that monitors the keywords the user searches for. Google can then show advertisements relevant to the user’s search, generating traffic toward the page of the company that invested in the service.
• Customer journey in support of SEO Specialists
UberSuggest is a partly free tool that allows you to track the keywords that allow a website to rank among the top results in the Google SERP or other search engines. By identifying the main terms used, one can guess what information, products or services users are looking for on the web and attempt to rank among the top results.
Stay in wonderland
Let me show you how deep the rabbit hole goes.
Check out more of the Innovation Alphabet:

3D Printing
3D Printing
“3D printing” is a process carried out by an electronic device which, instead of resorting to the canonical ink, it molds almost any kind of material: from concrete to living tissue, most usually plastic, but also metal. And the operating principle is similar to that of a traditional printer. The creation of three-dimensional models can lead to the redesign of a company’s production capabilities.
Dive In
5G
5G
5G is the new frontier of cellular telephony. It was designed to improve (or completely replace) previous generations of mobile networks. The 5th generation features lower latency, ensuring flawless performance of business applications and many other digital experiences – thus enabling the new cultural generations to furiously play Fortnite away from home.
Dive In
Advanced Analytics
Advanced Analytics
The term “Advanced Analytics” refers to the ability to autonomously or semi-autonomously analyze data and content to identify correlations, develop analyses, predictions, and recommendations. It is not just a matter of collecting information and then organizing it into watertight compartments: the ultimate goal is to identify a dialogue pattern from a data-driven perspective.
Dive In
Agile
Agile
Agile is an approach to software development designed to respond to change. Teams quickly analyze the context in which they operate, identify uncertainties faced, and figure out how to adapt to always move forward. Interaction between individuals comes before processes and tools; collaboration with the customer is more important than negotiating contracts.
Dive In
Ansoff Matrix
Ansoff Matrix
The Ansoff Matrix is a marketing planning model that arises from the intersection of new and existing products and markets. It derives four possible strategies for expanding the company’s market, which are built around four variables with a changeable factor of risks and possibilities: existing product, new product, existing market, new market.
Dive In
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence is not strictly defined. Basically, it is a computer system able to make decisions in an independent and flexible way. A good AI application can perform everyday tasks better than an average person (e.g., identifying other people from their photos on social media or beating the best chess player). Nothing to fear, then. Unless you are a chess champion.
Dive In
Artificial Scarcity
Artificial Scarcity
We often tend to desire what we cannot have. Or what we are in danger of losing: Artificial Scarcity is a strategy that flaunts a limited number of items that do not correspond to actual availability. The goal is to stimulate the perception in consumers that the stock of items is about to run out and thus create a need based on the “fear of being cut off” or the intention to buy the item in order to resell it at a higher price.
Dive In
Attack Surface
Attack Surface
The term attack surface refers to the part of a system that may be subject to attack or breach by hackers. The smaller that surface is, the easier it will be to protect it. Indeed, the Internet is an ocean of deep, dark waters: those who navigate it must be aware that they are exposing themselves to a flood of digital risks. Yet, ironically, we do not need a big boat to shelter us.
Dive In
Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality is an ever-evolving technology that overlays multimedia information on top of our common sensory horizon to gain a deeper understanding of our surroundings. No, it doesn’t allow you to step out of the Matrix dream simulation, nor can it be accessed by swallowing a red pill. But neither is it the disturbing experience of the Playtest episode of Black Mirror.
Dive In
Balanced Scorecard
Balanced Scorecard
In business, as in life, you need balance. The Balanced Scorecard is a holistic tool for strategic management. It offers, in fact, the possibility of assessing corporate performance in its wholeness. An overview that embraces four perspectives: the business/financial side, customers and stakeholders, internal processes, and learning and growth.
Dive In