Innovation Alphabet
5G
In a nutshell
5G is the new frontier of cellular telephony. It was designed to improve (or completely replace) previous generations of mobile networks. The 5th generation features lower latency, ensuring flawless performance of business applications and many other digital experiences – thus enabling the new cultural generations to furiously play Fortnite away from home.


5g networks
First of all, not all 5G networks are equal. We need to set a difference between the super fast mmWave 5G and the slower but more widespread Sub-6GHz 5G. The former refers to higher frequency radio bands while the latter refers to mid and low-frequency bands under 6GHz.
Yeah, but what does it mean? It means that mmWave 5G networks are ultra-fast, but they’re also ultra-short range. To use mmWave technology, you need to be within about a block of a 5G tower, and that isn’t feasible in suburban and rural areas. Moreover, the spectrum is blocked and obscured by doors, windows, trees, and walls, further limiting its available range.
Instead, Sub-6GHz 5G is faster than 4G, but it doesn’t offer the amazingly fast speeds you can get with mmWave. Also, since it has a longer range and can better penetrate objects, it is much more affordable for carriers to implement.

Application Fields
• Smart factories: Setting up interconnected, efficient, and semi-automated smart factories would be impossible without a strong network architecture. 5G is the key to harness the pervasive connectivity of the Internet of Things, delivering unprecedented levels of productivity. Digitalization, process automation and innovative services are indispensable for the business of smart industries today.
• Smart cities: The fifth generation is thinking big and is not limited to factories. “Smart cities” will be, according to the European Commission, places where “traditional networks and services are made more efficient using digital and telecommunications technologies for the benefit of its inhabitants and businesses”. 5G stands as a solver of problems that were insurmountable for previous networks. For example, poor support for simultaneous connections, high power consumption and too high price per bit.
• Healthcare: The use of 5G in health care enables an efficient networked monitoring of all medical devices. This allows, for example, real-time blood tests in chemotherapy to be analyzed by Artificial Intelligence systems. But the new technology also will enable applications that were totally sci-fi back in the days of Dr. House: telemedicine, remote surgery, home drug delivery. It will be the 4Ps medicine: predictive, preventive, personalized and participatory.
Industries
• 5G in Smart Homes
Smart Bin and Smart Gate are two prototype solutions designed by Polifactory – a research laboratory of the Politecnico di Milano. Together with Vodafone, Exprivia Italtel, Prisma Telecom Testing and with the support of Amazon Web Services, they aimed respectively at sorted waste collection and people flow monitoring. Smart Bin leverages the potential of 5G and Artificial Intelligence to automate and speed up waste sorting; Smart Gate, on the other hand, combines environmental monitoring and people flow detection features by cluster.
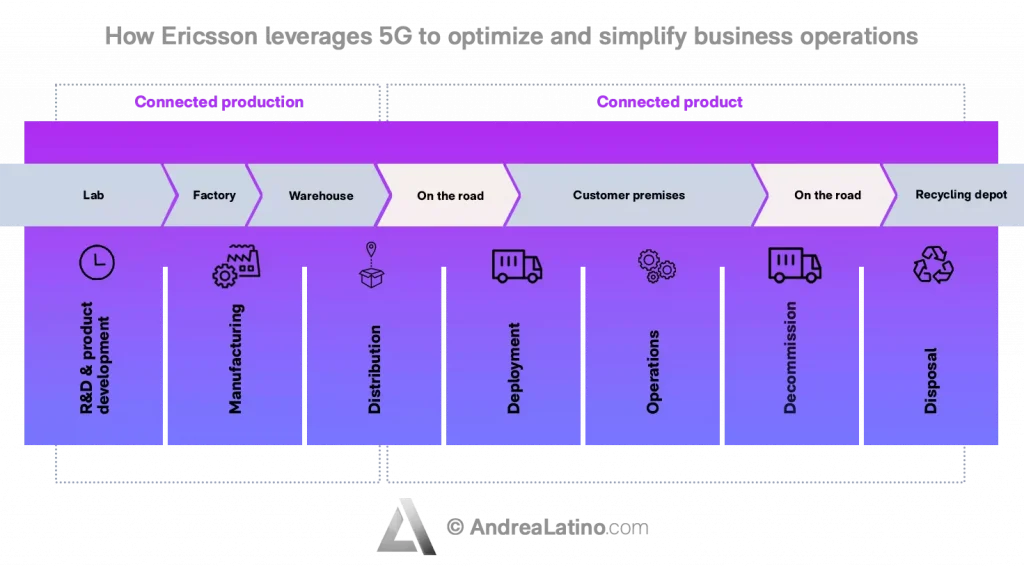
• 5G in the Telecommunications Industry – Ericsson Industry Connect
Companies implementing Industry 4.0 must have fast, reliable, and secure wireless connectivity solutions at their disposal. Ericsson, therefore, has devised a fifth-generation technology designed specifically for industrial environments so that enterprises can benefit from a network that allows them to optimize and simplify business operations through the creation, collection, and analysis of data.
Do you have a Strategy & Innovation challenge to tackle? Let’s face it. Together.
C-levels from these companies (AND MORE) relied on my expertise to overcome thEIR CHALLENGES IN THIS AREA. And you can, too.
Can I help you?Business Functions
• 5G in support of supply chain optimization
Marco Contento is the VP of 5G technologies at Telit – an Internet of Things (IoT) Enabler company headquartered in Irvine, California. And indeed he seems quite happy with the benefits that low-latency 5G connectivity brings to the supply chain. For example, he talks about vehicle-to-vehicle communication. Or, again, “an automotive factory synchronizing parts delivery from outside can see shipment status and integrate that tracking data into its workflow”. In short, 5G helps improve visibility in supply chains and prevents inventory shrink.
• 5G in support of earthquake prevention
The University of L’Aquila, in partnership with ZTE and Wind Tre, has implemented a system to monitor stability and structural safety of buildings through sensors that transmit signals at very high speed through 5G to a data processing center. The monitoring of the situation will be immediate: in the event of a tremor, seismic waves would be detected by the sensors, consequently setting in motion a whole chain of safety interventions. All of this within milliseconds. And that’s a previously unthinkable speed that is crucial to save lives.
• 5G in support of manufacturing
With the 5G-SMART project, Ericsson wants to test the new network technology in real production environments and in its most sophisticated applications such as remote-controlled industrial robotics, wireless process monitoring, and mobile robotics. They conduct tests on-site, bringing the appropriate instrumentation inside factories and machine rooms, and performing Electromagnetic Compatibility assessments, signal measurements and coexistence tests between public and private industrial networks.
Stay in wonderland
Let me show you how deep the rabbit hole goes.
Check out more of the Innovation Alphabet:

3D Printing
3D Printing
“3D printing” is a process carried out by an electronic device which, instead of resorting to the canonical ink, it molds almost any kind of material: from concrete to living tissue, most usually plastic, but also metal. And the operating principle is similar to that of a traditional printer. The creation of three-dimensional models can lead to the redesign of a company’s production capabilities.
Dive In
5G
5G
5G is the new frontier of cellular telephony. It was designed to improve (or completely replace) previous generations of mobile networks. The 5th generation features lower latency, ensuring flawless performance of business applications and many other digital experiences – thus enabling the new cultural generations to furiously play Fortnite away from home.
Dive In
Advanced Analytics
Advanced Analytics
The term “Advanced Analytics” refers to the ability to autonomously or semi-autonomously analyze data and content to identify correlations, develop analyses, predictions, and recommendations. It is not just a matter of collecting information and then organizing it into watertight compartments: the ultimate goal is to identify a dialogue pattern from a data-driven perspective.
Dive In
Agile
Agile
Agile is an approach to software development designed to respond to change. Teams quickly analyze the context in which they operate, identify uncertainties faced, and figure out how to adapt to always move forward. Interaction between individuals comes before processes and tools; collaboration with the customer is more important than negotiating contracts.
Dive In
Ansoff Matrix
Ansoff Matrix
The Ansoff Matrix is a marketing planning model that arises from the intersection of new and existing products and markets. It derives four possible strategies for expanding the company’s market, which are built around four variables with a changeable factor of risks and possibilities: existing product, new product, existing market, new market.
Dive In
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence is not strictly defined. Basically, it is a computer system able to make decisions in an independent and flexible way. A good AI application can perform everyday tasks better than an average person (e.g., identifying other people from their photos on social media or beating the best chess player). Nothing to fear, then. Unless you are a chess champion.
Dive In
Artificial Scarcity
Artificial Scarcity
We often tend to desire what we cannot have. Or what we are in danger of losing: Artificial Scarcity is a strategy that flaunts a limited number of items that do not correspond to actual availability. The goal is to stimulate the perception in consumers that the stock of items is about to run out and thus create a need based on the “fear of being cut off” or the intention to buy the item in order to resell it at a higher price.
Dive In
Attack Surface
Attack Surface
The term attack surface refers to the part of a system that may be subject to attack or breach by hackers. The smaller that surface is, the easier it will be to protect it. Indeed, the Internet is an ocean of deep, dark waters: those who navigate it must be aware that they are exposing themselves to a flood of digital risks. Yet, ironically, we do not need a big boat to shelter us.
Dive In
Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality is an ever-evolving technology that overlays multimedia information on top of our common sensory horizon to gain a deeper understanding of our surroundings. No, it doesn’t allow you to step out of the Matrix dream simulation, nor can it be accessed by swallowing a red pill. But neither is it the disturbing experience of the Playtest episode of Black Mirror.
Dive In
Balanced Scorecard
Balanced Scorecard
In business, as in life, you need balance. The Balanced Scorecard is a holistic tool for strategic management. It offers, in fact, the possibility of assessing corporate performance in its wholeness. An overview that embraces four perspectives: the business/financial side, customers and stakeholders, internal processes, and learning and growth.
Dive In