Innovation Alphabet
Internet of Things
In a nutshell
Given the variety of possible applications, standards and specific infrastructures, it is complicated to identify a single definition of “Internet of Things.” It could be defined as a network of objects equipped with identification technologies that interact with each other through an internet connection, with the purpose of transferring information in the form of data (huh?). In short, it is about devices evolving, becoming smarter to make our lives easier.

Application Fields
• Healthcare: Much attention is being paid to the monitoring of disease carriers. Increasing the connectivity of medical devices allows for direct communication with the doctor.
• Transportation: Smart cars represent the biggest challenge for automakers. Indeed, they combine the potential of automated driving and the potential of the connected car. They accumulate data and communicate real-time diagnoses, directly alerting the tire dealer if you get a flat tire or the repair shop if the engine is not working as it should. Smart cars also have insurance implications. They collect information about one’s driving skills that, if optimal, could save him or her money on insurance.
• Domotics: Connecting appliances and everyday objects through home automation managers make our homes smart. Sensors connected through smartphones or other devices allow the home’s temperature, lights and even windows to be controlled. They can alert the homeowner to events happening while he or she is anywhere else.
Do you have a Strategy & Innovation challenge to tackle? Let’s face it. Together.
C-levels from these companies (AND MORE) relied on my expertise to overcome thEIR CHALLENGES IN THIS AREA. And you can, too.
Can I help you?Industries
• Internet of Things in wine farms
Ericsson, together with Intel, Telenor Connexion and MyOmega, has designed a complete cloud-based service aimed at collecting data on air and soil moisture, temperature, and sunlight intensity. This is done through sensors and gateways for the Internet of Things, enabling winemakers to perform predictive analytics, improve resource management and enable real-time remote monitoring.
• Internet of Things in the pharmaceutical industry
Worldwide, 235 million people suffer from asthma. Since it is an incurable condition, regular medical checkups are necessary. The most common asthma treatment is an inhaler, the use of which is effective if done at the right time. But often this is not the case. MyAirCoach is an EU-supported initiative testing smart inhalers that can predict a potential asthma attack a week in advance by analyzing environmental conditions (pollution, temperature, and humidity) and the vital parameters of the patients themselves.
• Internet of Things in the power industry
China Mobile, China’s largest mobile operator, has applied the Internet of Things to public lighting through LED technology in several cities in China, such as Longnan, Bahzou and Guizhou. This measure has resulted in several benefits. For example, through the use of special twilight and motion sensors, city streets are lit only when needed – the system is able to self-regulate when a vehicle or pedestrian passes by. It also allows monitoring of air quality and even traffic, thanks to the GPS linking the light poles together.
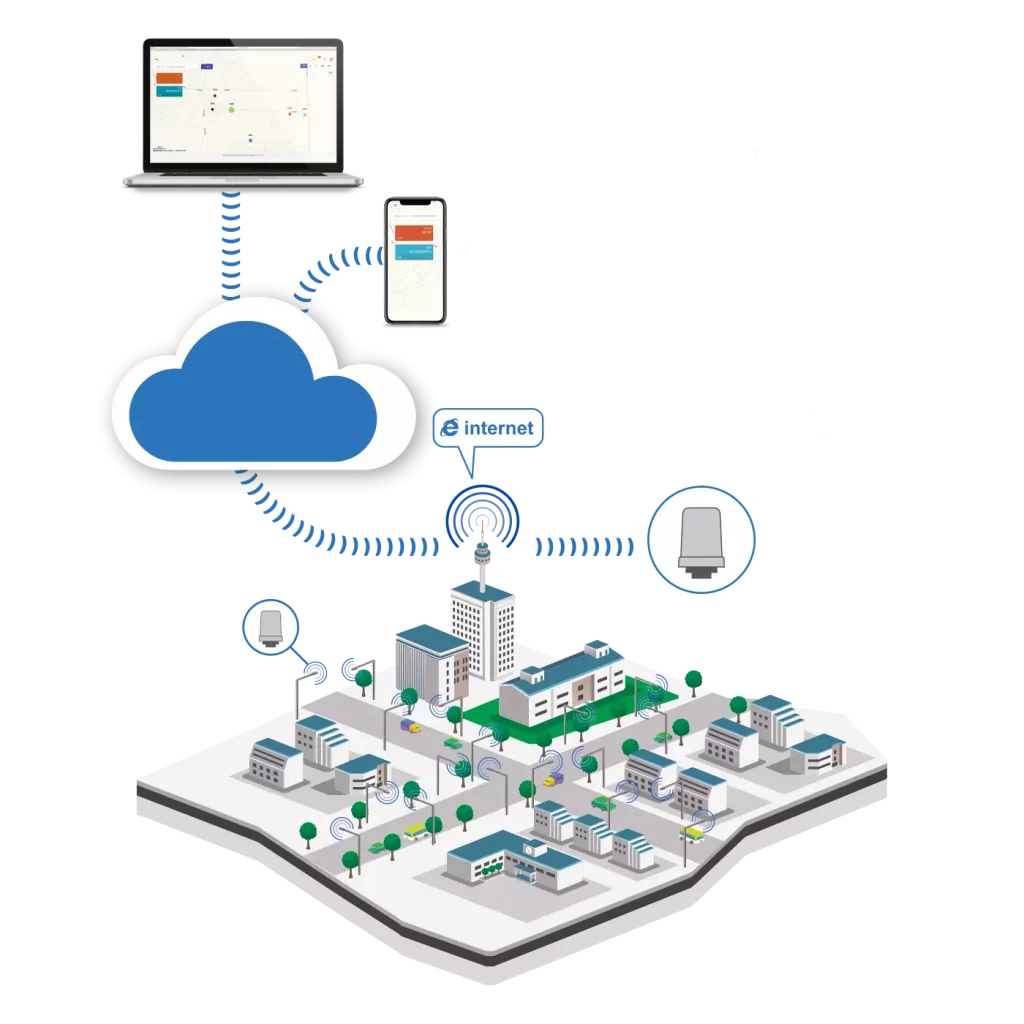
Business Functions
• Internet of Things in support of marketing
Heineken leveraged IoT technology to create a dynamic and participatory marketing experience. By placing a number of beer bottles connected to a GPS device on the streets of Amsterdam, the company created a sort of treasure hunt in order to increase the number of visitors to its museum. In fact, the competition was designed to have the tourists finish the competition at the Heineken Experience Museum.
• Internet of Things in support of HR
Servair, an international company specializing in airline catering, improved flow management by automating cargo receiving and vehicle movement. The Internet of Things has helped streamline operations and increase airport security. Once again, objects go from passive to active and, more importantly, intelligent. They participate in production processes by transferring data and maintaining an information link, so that they work alongside the workforce of operational processes.
• Internet of Things in support of management
Nestlé, a world leader in the food industry, has applied the Internet of Things in agriculture and, more specifically, in tomato growing. The goal? To regulate the degree of acidity inside the fruit. Basically, sensors on agricultural drones allow them to detect water stress and pest outbreaks. Later, the same drones can carry out treatments on the specific areas where the problem occurs. By applying this technology, it benefits the company’s agribusiness management department. In fact, a control system that, manually-wise, would involve great effort and large margins for error, is here automated.
Stay in wonderland
Let me show you how deep the rabbit hole goes.
Check out more of the Innovation Alphabet:

3D Printing
3D Printing
“3D printing” is a process carried out by an electronic device which, instead of resorting to the canonical ink, it molds almost any kind of material: from concrete to living tissue, most usually plastic, but also metal. And the operating principle is similar to that of a traditional printer. The creation of three-dimensional models can lead to the redesign of a company’s production capabilities.
Dive In
5G
5G
5G is the new frontier of cellular telephony. It was designed to improve (or completely replace) previous generations of mobile networks. The 5th generation features lower latency, ensuring flawless performance of business applications and many other digital experiences – thus enabling the new cultural generations to furiously play Fortnite away from home.
Dive In
Advanced Analytics
Advanced Analytics
The term “Advanced Analytics” refers to the ability to autonomously or semi-autonomously analyze data and content to identify correlations, develop analyses, predictions, and recommendations. It is not just a matter of collecting information and then organizing it into watertight compartments: the ultimate goal is to identify a dialogue pattern from a data-driven perspective.
Dive In
Agile
Agile
Agile is an approach to software development designed to respond to change. Teams quickly analyze the context in which they operate, identify uncertainties faced, and figure out how to adapt to always move forward. Interaction between individuals comes before processes and tools; collaboration with the customer is more important than negotiating contracts.
Dive In
Ansoff Matrix
Ansoff Matrix
The Ansoff Matrix is a marketing planning model that arises from the intersection of new and existing products and markets. It derives four possible strategies for expanding the company’s market, which are built around four variables with a changeable factor of risks and possibilities: existing product, new product, existing market, new market.
Dive In
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence is not strictly defined. Basically, it is a computer system able to make decisions in an independent and flexible way. A good AI application can perform everyday tasks better than an average person (e.g., identifying other people from their photos on social media or beating the best chess player). Nothing to fear, then. Unless you are a chess champion.
Dive In
Artificial Scarcity
Artificial Scarcity
We often tend to desire what we cannot have. Or what we are in danger of losing: Artificial Scarcity is a strategy that flaunts a limited number of items that do not correspond to actual availability. The goal is to stimulate the perception in consumers that the stock of items is about to run out and thus create a need based on the “fear of being cut off” or the intention to buy the item in order to resell it at a higher price.
Dive In
Attack Surface
Attack Surface
The term attack surface refers to the part of a system that may be subject to attack or breach by hackers. The smaller that surface is, the easier it will be to protect it. Indeed, the Internet is an ocean of deep, dark waters: those who navigate it must be aware that they are exposing themselves to a flood of digital risks. Yet, ironically, we do not need a big boat to shelter us.
Dive In
Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality is an ever-evolving technology that overlays multimedia information on top of our common sensory horizon to gain a deeper understanding of our surroundings. No, it doesn’t allow you to step out of the Matrix dream simulation, nor can it be accessed by swallowing a red pill. But neither is it the disturbing experience of the Playtest episode of Black Mirror.
Dive In
Balanced Scorecard
Balanced Scorecard
In business, as in life, you need balance. The Balanced Scorecard is a holistic tool for strategic management. It offers, in fact, the possibility of assessing corporate performance in its wholeness. An overview that embraces four perspectives: the business/financial side, customers and stakeholders, internal processes, and learning and growth.
Dive In