Innovation Alphabet
Blockchain
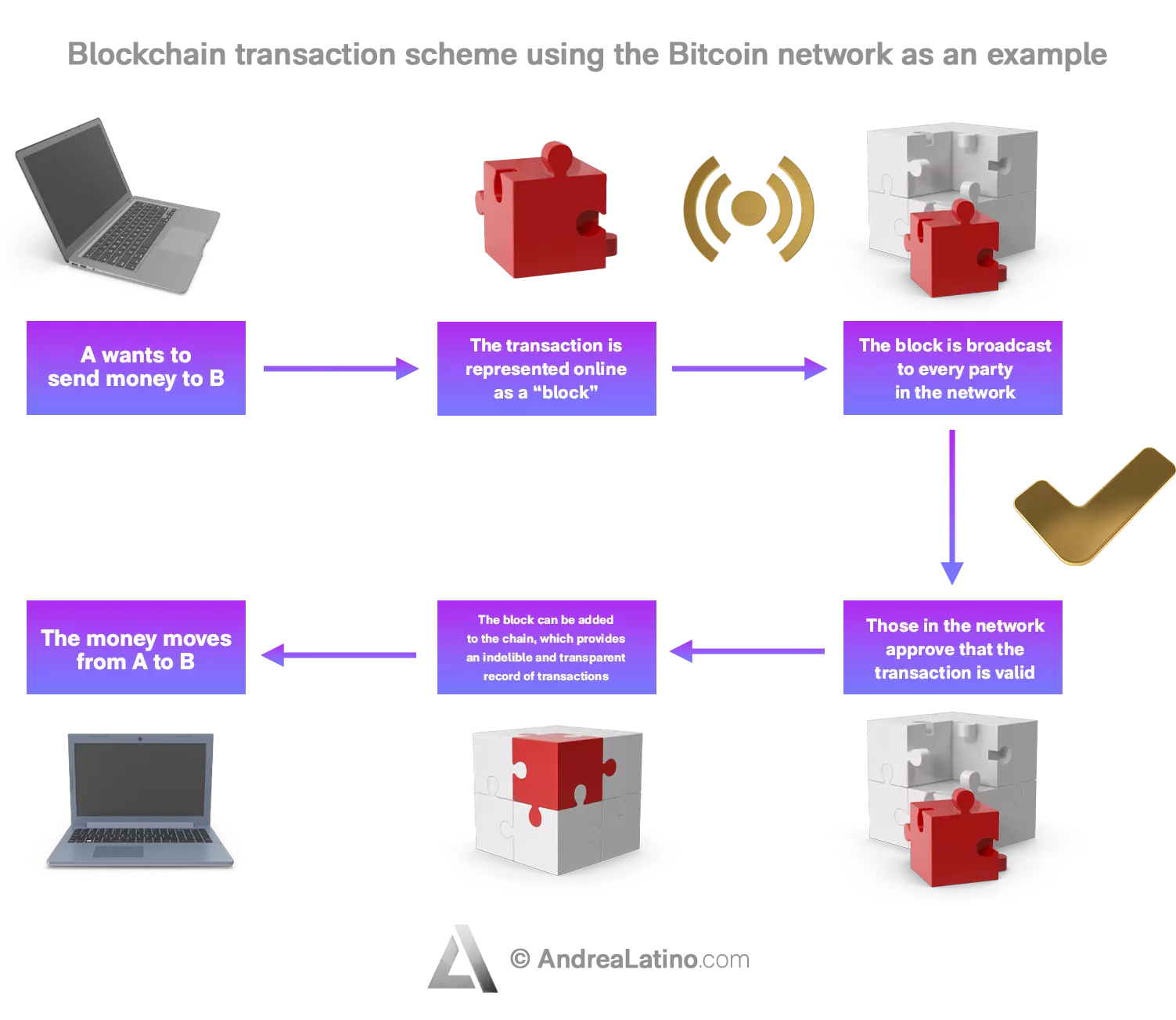
In a nutshell
A shared and immutable ledger within which nothing can be lost. The blockchain, often known in correlation with bitcoin and cryptocurrencies, today represents a giant decentralized catalog of interlinked data and information. It facilitates the recording of transactions and tracking of assets in a commercial network, reducing risks and costs for everyone involved.


private vs public
A major difference
As you can guess, the main difference lies in the level of access given to users. But, as a company, you have to identify and understand how these differ in order to select the rigth platform. So, let’s try to unchain the solution.
What is a public blockchain?
A public blockchain is an open network where anyone can access the chain and add blocks whenever they want. Bitcoin and Ethereum are both examples of public blockchains. They are decentralized and there is not a single entity which controls the network. But let’s see some other features:
- • Security: transactions are immutable because they cannot be altered or removed, only added. Also, their validity is recognised when the majority agree that the transaction is valid.
- • Anonymous nature: every one is anonymous. You don’t have to use your real name. Everything would stay hidden, and no one can track you based on that.
- • Transparency: the platforms allow you to see the ledger anytime you want. There is no scope for corruption or discrepancies.
What is a private blockchain?
A private blockchain has a centralised network that quickens the transaction process. The network is managed by an administrator and participants need consent to join it. Ripple and Hyperledger are both examples of private blockchain. Probably, the best feature is about speed – a smaller set of users means less time to reach a consensus to validate a transaction. But it’s not just that:
- • Better scalability: the opportunity to add nodes and services on demand can provide a great advantage.
- • High efficiency: private blockchains only allow a handful of people in the network. Public blockchain, on the other hand, introduce everyone to the network. Thus, it slows down rapidly.
- • Full privacy: private blockchain solutions tend to focus on privacy concerns. Hence, If you are looking for a technology that can offer the highest level of privacy, here you go.
Blockchain-as-a-service
A relatively new development in the growing field of blockchain technology is Blockchain-as-a-service (BaaS). The term referes to a managed blockchain platform allowing buyers to leverage cloud-based solutions in order for them to build, host, and operate their own blockchain apps and related functions on the blockchain. Meanwhile, the cloud-based service provider keeps the infrastructure agile and operational.
You can easily understand why BaaS can boost blockchain adoption across businesses. In particular, Hyperledger is an open source project born to support the development of blockchain-based distributed ledgers. It was created by the Linux Foundation in 2016. Hyperledger-based technology works using five layers.
1) A consensus layer, which makes an agreement on order and confirms the validity of the transactions in a block.
2) A smart contract layer, which processes and authorizes transaction requests.
3) A communication layer, which manages peer-to-peer message transport.
4) An Application Program Interface, which allows other applications to communicate with the blockchain.
5) Identity management services, in order to validate the identities of users and systems.
Application Fields
• Payments and money transfers: You surely know blockchains in correlation with bitcoin and cryptocurrencies. In fact, it is the universe that has prompted their evolution and experimentation. Bitcoin consists of a decentralized, uncensored, secure, and programmable value recording and exchange system. It makes it possible to create direct payment flows between originators and beneficiaries, without intermediaries, at ultra-cheap rates and near-instantaneous speed.
• Car sharing: These services are based on the possibility of renting cars for a short period of time. Usually, you can find the available cars scattered around the city in reserved parking lots. One of the big problems faced by car sharing companies is the lack of reliability on the part of the user. By using blockchain, however, you can address the risk of fraud. The technology offers a quick and secure way to create a binding financial agreement through “smart contracts”. Blockchain thus guarantees payment and enables transparent use of cars.
• Stock trading: Blockchain technology applied to the buying and selling of equities can automate the process of buying, selling, and trading in a way that ensures greater efficiency within the stock market.
Industries
• Blockchain in the pharmaceutical industry
UCLA Health is an academic medical center in the Los Angeles area that boasts an extensive primary care network in the U.S. In addition to healthcare, the center also decided to put the security of their patients’ data first by leveraging the blockchain system. The implementation of this technology, combined with artificial intelligence, allows data sharing while protecting privacy.
• Blockchain in the energy industry
New York-based start-up Transactive Grid offers a grid energy storage service based on the open source Ethereum platform. Transactive Grid deals primarily with energy produced from renewable sources. Renewable energy producers are linked together to create a kind of micro-grid where people can buy and sell electricity. A movement aimed at forming a small community in which producers and consumers work together. They buy and sell renewable energy according to each other’s needs. Energy production and related transactions are tracked using “smart contracts” promoted by Ethereum’s blockchain technology. In this way, every unit of energy produced and transmitted in the microgrid will remain for eternity.
• Blockchain in the service industry
Dnata (Dubai National Air Transport Association) is a multinational company operating in the air transport services industry involved in handling, catering, cargo, and travel agency. The company used the blockchain solution to eliminate redundant data and improve visibility and transparency of cargo services. They achieved the output precisely because of the technology adopted. Through the digitalization of the supply chain, it uses a peer-to-peer network to monitor and manage the route of each container.
Do you have a Marketing & Sales challenge to tackle? Let’s face it. Together.
C-levels from these companies (AND MORE) relied on my expertise to overcome thEIR CHALLENGES IN THIS AREA. And you can, too.
Can I help you?Business Functions
• Blockchain in support of marketing
Even the fashion world meets blockchain technology. Babyghost is a fashion brand that during Shanghai Fashion Week 2016 collaborated with the VeChain platform to defend product authenticity and protect patents and intellectual property. A collaboration that, first and foremost, demonstrates how the scope of blockchain does not stop at financial services. The result was a multi-sensory celebration. As each Babyghost garment was embedded with a VeChain chip, attendees had the unique opportunity to scan the chip to receive an interactive designer memento.

• Blockchain in support of HR
Recruit, a Japan-based Human Resources company, is using blockchain technology to check the veracity of previous work experience found inside the resumes of new applicants. This is possible through the development of cryptographic certificates that attest to the authenticity of qualifications and resumes, based on the way blockchain works. This enables the construction of a more transparent and easily verifiable recruiting system.
• Blockchain in support of management
Provenance, a global leader in sustainable marketing technology, has developed a traceability system that serves supply management to make supply chains more transparent. The aim is to create more trust between companies and customers. As blockchain technology enables clearer and more secure control of transactions, operations between different players in a supply chain – from production to sale – can be documented in a decentralized ledger. This would reduce transcription costs, delays, and possible human mistakes.
Stay in wonderland
Let me show you how deep the rabbit hole goes.
Check out more of the Innovation Alphabet:

3D Printing
3D Printing
“3D printing” is a process carried out by an electronic device which, instead of resorting to the canonical ink, it molds almost any kind of material: from concrete to living tissue, most usually plastic, but also metal. And the operating principle is similar to that of a traditional printer. The creation of three-dimensional models can lead to the redesign of a company’s production capabilities.
Dive In
5G
5G
5G is the new frontier of cellular telephony. It was designed to improve (or completely replace) previous generations of mobile networks. The 5th generation features lower latency, ensuring flawless performance of business applications and many other digital experiences – thus enabling the new cultural generations to furiously play Fortnite away from home.
Dive In
Advanced Analytics
Advanced Analytics
The term “Advanced Analytics” refers to the ability to autonomously or semi-autonomously analyze data and content to identify correlations, develop analyses, predictions, and recommendations. It is not just a matter of collecting information and then organizing it into watertight compartments: the ultimate goal is to identify a dialogue pattern from a data-driven perspective.
Dive In
Agile
Agile
Agile is an approach to software development designed to respond to change. Teams quickly analyze the context in which they operate, identify uncertainties faced, and figure out how to adapt to always move forward. Interaction between individuals comes before processes and tools; collaboration with the customer is more important than negotiating contracts.
Dive In
Ansoff Matrix
Ansoff Matrix
The Ansoff Matrix is a marketing planning model that arises from the intersection of new and existing products and markets. It derives four possible strategies for expanding the company’s market, which are built around four variables with a changeable factor of risks and possibilities: existing product, new product, existing market, new market.
Dive In
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence is not strictly defined. Basically, it is a computer system able to make decisions in an independent and flexible way. A good AI application can perform everyday tasks better than an average person (e.g., identifying other people from their photos on social media or beating the best chess player). Nothing to fear, then. Unless you are a chess champion.
Dive In
Artificial Scarcity
Artificial Scarcity
We often tend to desire what we cannot have. Or what we are in danger of losing: Artificial Scarcity is a strategy that flaunts a limited number of items that do not correspond to actual availability. The goal is to stimulate the perception in consumers that the stock of items is about to run out and thus create a need based on the “fear of being cut off” or the intention to buy the item in order to resell it at a higher price.
Dive In
Attack Surface
Attack Surface
The term attack surface refers to the part of a system that may be subject to attack or breach by hackers. The smaller that surface is, the easier it will be to protect it. Indeed, the Internet is an ocean of deep, dark waters: those who navigate it must be aware that they are exposing themselves to a flood of digital risks. Yet, ironically, we do not need a big boat to shelter us.
Dive In
Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality is an ever-evolving technology that overlays multimedia information on top of our common sensory horizon to gain a deeper understanding of our surroundings. No, it doesn’t allow you to step out of the Matrix dream simulation, nor can it be accessed by swallowing a red pill. But neither is it the disturbing experience of the Playtest episode of Black Mirror.
Dive In
Balanced Scorecard
Balanced Scorecard
In business, as in life, you need balance. The Balanced Scorecard is a holistic tool for strategic management. It offers, in fact, the possibility of assessing corporate performance in its wholeness. An overview that embraces four perspectives: the business/financial side, customers and stakeholders, internal processes, and learning and growth.
Dive In