Innovation Alphabet
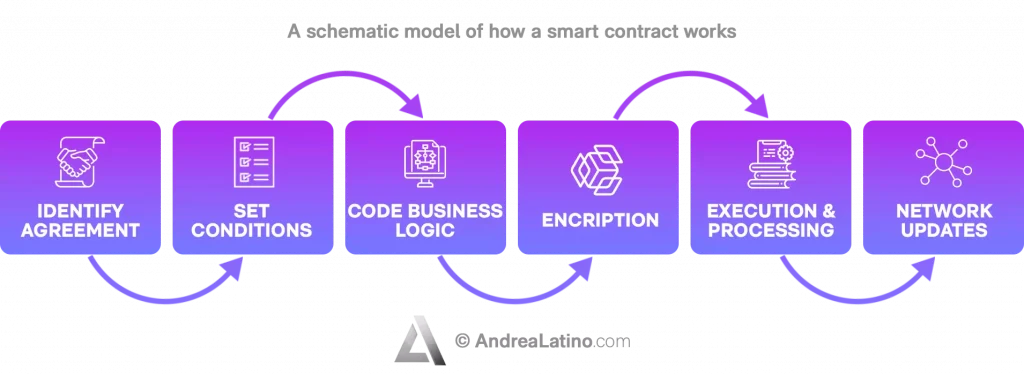
Smart Contract
In a nutshell
If-this-then-that: this is the logic on which smart contracts – a technological application that operates on the blockchain system to automate the performance of contractual services – are based. A series of clauses are translated into code inside a software, so as to bind the parties to comply with the contract. Independence, unmodifiability, cost savings.


Application Fields
• Insurance Sector: A smart contract is based on a code that “reads” the contractual clauses and operating modes in which the agreed conditions must occur. The contract is automatically executed when the data referring to the actual situations correspond to the data referring to the conditions and clauses reported. The smart contract, consequently, is independent from intermediaries (notaries and lawyers) during the verification and approval stage, although legal support is still necessary for its drafting.
• Banking industry: Contract automation is a huge advantage for the banking field, as it avoids the use of intermediaries, drastically reducing transactional costs. Banking services lend themselves particularly well to being digitalized and automated in an integrated and decentralized digital environment such as blockchain technology.
• Sharing economy: When making online purchases, payment is transferred only if the product has been successfully delivered. Sharing economy services could benefit a lot from smart contracts because they would ensure security and compliance.
Industries
• Smart contract in the financial industry
Ethereum has become the blockchain of reference for the creation of smart contracts (more than 200,000 “signed” as of today). Ether is the virtual currency unit, serving both as a cryptocurrency and a power generator. Smart contracts, in order to function, must pay for the use of the network’s computing power through the related digital currency. Contracts can cover financial transactions but also domain registration, election systems, crowdfunding and more.
• Smart contract in the digital industry
Blockchain Technology Partners is an organization that aims to reduce transaction costs and complexity through decentralization while ensuring trust, transparency, and accountability.
• Smart contract in the IT industry
Digital Asset is an American startup that focuses on DAML, an intuitive programming language for smart contracts. It digitalizes agreements between parties and safely automate transactions. Digital Asset enables large companies to leverage the power of Distributed Ledger Technology to streamline business operations and make value transfers efficient and secure.
Do you have a Public Affairs & Comms challenge to tackle? Let’s face it. Together.
C-levels from these companies (AND MORE) relied on my expertise to overcome thEIR CHALLENGES IN THIS AREA. And You can, too.
Can I help you?Business Functions
• Smart contract in support of supply chain management
Covantis has implemented blockchain solutions to efficiently execute trade operations and document management. Stakeholders will exchange documents and information more quickly. The technology has improved by 60 percent in automated tasks, 70 percent in transaction speed, and 80 percent in error reduction.
• Smart contract in support of insurance
Stratumn is a French startup that, after winning over BNP Paribas Cardif’s C. Entrepreneurs fund as well, is trying to implement the largest trial of blockchain network for insurance involving 14 companies. Stratumn’s technology promises to redesign end-to-end process management and aims to address privacy compliance issues through its advanced encryption system.
• Smart contract in support of trade exchanges
Japanese insurance company Tokio Marine & Fire Insurance Nichido, in collaboration with NTT Data Corporation, has begun experimenting the use of blockchain for policies in the commercial trade sector, especially maritime trade.
Stay in wonderland
Let me show you how deep the rabbit hole goes.
Check out more of the Innovation Alphabet:

3D Printing
3D Printing
“3D printing” is a process carried out by an electronic device which, instead of resorting to the canonical ink, it molds almost any kind of material: from concrete to living tissue, most usually plastic, but also metal. And the operating principle is similar to that of a traditional printer. The creation of three-dimensional models can lead to the redesign of a company’s production capabilities.
Dive In
5G
5G
5G is the new frontier of cellular telephony. It was designed to improve (or completely replace) previous generations of mobile networks. The 5th generation features lower latency, ensuring flawless performance of business applications and many other digital experiences – thus enabling the new cultural generations to furiously play Fortnite away from home.
Dive In
Advanced Analytics
Advanced Analytics
The term “Advanced Analytics” refers to the ability to autonomously or semi-autonomously analyze data and content to identify correlations, develop analyses, predictions, and recommendations. It is not just a matter of collecting information and then organizing it into watertight compartments: the ultimate goal is to identify a dialogue pattern from a data-driven perspective.
Dive In
Agile
Agile
Agile is an approach to software development designed to respond to change. Teams quickly analyze the context in which they operate, identify uncertainties faced, and figure out how to adapt to always move forward. Interaction between individuals comes before processes and tools; collaboration with the customer is more important than negotiating contracts.
Dive In
Ansoff Matrix
Ansoff Matrix
The Ansoff Matrix is a marketing planning model that arises from the intersection of new and existing products and markets. It derives four possible strategies for expanding the company’s market, which are built around four variables with a changeable factor of risks and possibilities: existing product, new product, existing market, new market.
Dive In
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence is not strictly defined. Basically, it is a computer system able to make decisions in an independent and flexible way. A good AI application can perform everyday tasks better than an average person (e.g., identifying other people from their photos on social media or beating the best chess player). Nothing to fear, then. Unless you are a chess champion.
Dive In
Artificial Scarcity
Artificial Scarcity
We often tend to desire what we cannot have. Or what we are in danger of losing: Artificial Scarcity is a strategy that flaunts a limited number of items that do not correspond to actual availability. The goal is to stimulate the perception in consumers that the stock of items is about to run out and thus create a need based on the “fear of being cut off” or the intention to buy the item in order to resell it at a higher price.
Dive In
Attack Surface
Attack Surface
The term attack surface refers to the part of a system that may be subject to attack or breach by hackers. The smaller that surface is, the easier it will be to protect it. Indeed, the Internet is an ocean of deep, dark waters: those who navigate it must be aware that they are exposing themselves to a flood of digital risks. Yet, ironically, we do not need a big boat to shelter us.
Dive In
Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality is an ever-evolving technology that overlays multimedia information on top of our common sensory horizon to gain a deeper understanding of our surroundings. No, it doesn’t allow you to step out of the Matrix dream simulation, nor can it be accessed by swallowing a red pill. But neither is it the disturbing experience of the Playtest episode of Black Mirror.
Dive In
Balanced Scorecard
Balanced Scorecard
In business, as in life, you need balance. The Balanced Scorecard is a holistic tool for strategic management. It offers, in fact, the possibility of assessing corporate performance in its wholeness. An overview that embraces four perspectives: the business/financial side, customers and stakeholders, internal processes, and learning and growth.
Dive In