Innovation Alphabet
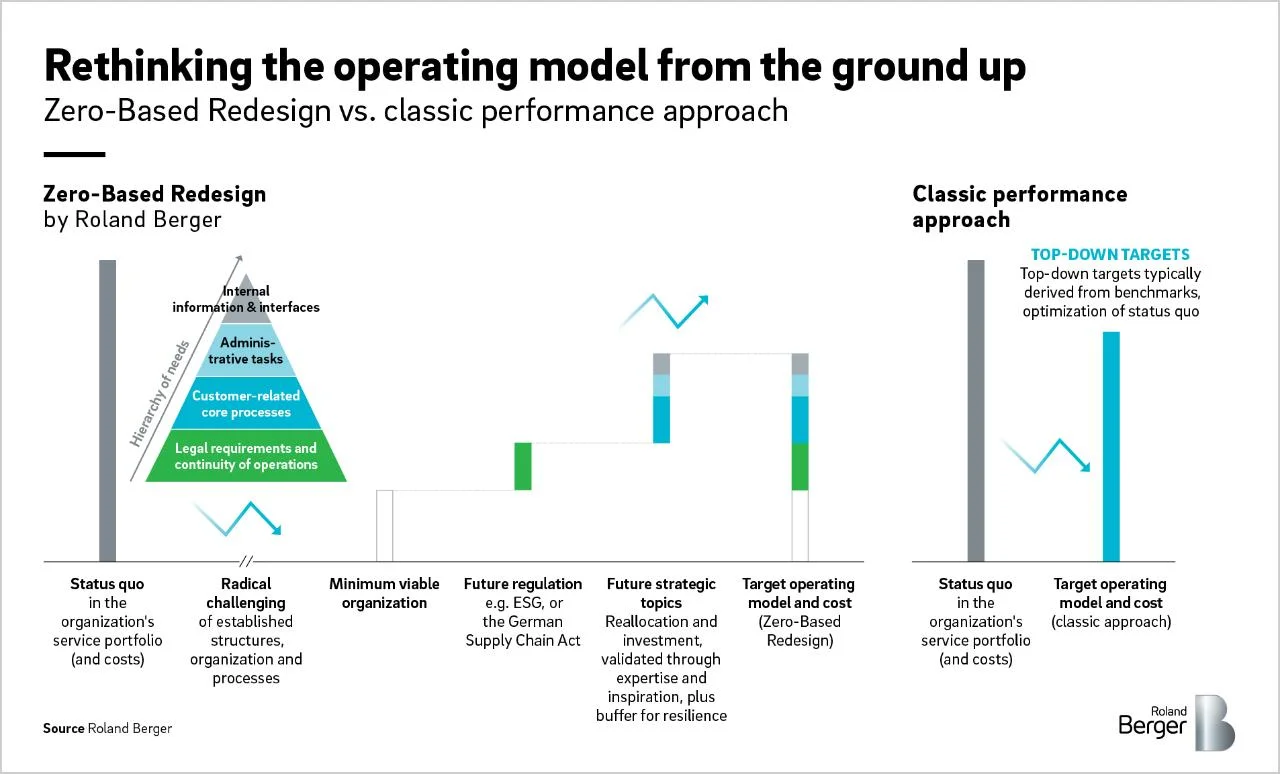
Zero-Based Redesign
In a nutshell
The Zero-Based Redesign approach refers to a restructuring that helps companies increase the likelihood of long-term success and prepares them for unexpected disruptions in the business. An evolved, no-frills, practical new operational asset. It prioritizes agility and vision for the future, transforms corporate culture by aligning internal priorities, and radically reforms the cost structure.


DEFINITION
A different interpretation of “starting over”
Usually, traditional efforts to streamline and simplify settle for incremental changes to the status quo. Savings tend to be temporary as costs come flooding back. Zero-Based Redesign, on the other hand, is a one-time effort that sets a brave ambition defined by core activities in delivering what customers value most about you. Organizational structure, governance, responsibilities and processes are integrated in order to satisfy your customers’ needs and optimize the efficiency of your front line, using the best existing technology.
The ZBR approach puts a company in the position of having to virtually rebuild a process from scratch, without considering any type of limitation from the standpoint of resources, budget, and skills. By doing so, reorganization managers think outside the box and try to redesign their enterprise according to a strategic optimum consisting of activities required to support function-level strategy. This step involves reinstating activities, for example, investments in company culture, that are deemed critical to pursuing business objectives.
Application Fields
• Strategy: The Zero-Based approach assists the execution of the company’s business plan by building a strategy capable of guiding day-to-day actions so that long-term goals are accomplished. As a result, it is essential to wipe the slate clean, eliminating all activities that are not necessary for optimizing the company and then starting new ones based on the goals set. For example, if the company sets digitalization as a goal, it will be necessary to support daily operations with investments to create a digital culture among employees.
• Transparency: Zero-Based Redesign enables transparency of operations inside an organization, as it adopts an end-to-end perspective on both internal and external costs. Companies can leverage traceability to redesign business processes, seizing the opportunity to automate workflows and thereby reduce costs.
• Calculated Revolution: Before adopting a Zero-Based approach and redesigning from scratch, it is important to understand the potential response of the organization. Only after that it would be possible to initiate a change management plan. Senior managers must verify that the new organizational structure can function properly and is capable of supporting future operations. Once the appropriate tests have been conducted, managers will be responsible for training and informing employees about the benefits of the new course.
Industries
• Zero-Based Redesign in the pharmaceutical industry
Pharmaceutical industries are usually cautious about integrating innovation within their business models. Yet a Zero-Based reorganization could bring a breath of fresh air to the industry, giving it an important and bold constructive change. In particular, it would enable:
– Choosing the right digital technologies and prioritizing tools that can automate and improve processes.
– Assessing the fit of technologies to determine the most profitable ones.
– Building prototypes to conduct testing and learning experiments, and then testing whether or not a particular solution is a good fit for the business.
• Zero-Based Redesign in the service industry
Delta Airlines, one of the largest U.S. airlines, revolutionized its structure by restarting from scratch to deal with two issues: rising fuel costs and declining passenger traffic due to stiff competition from low-cost airlines. As a result, the company was able to cut costs by more than $1.7 million, and introduced automation technologies that improved visibility and overall service and control levels of the company’s financial processes.
Do you have a Strategy & Innovation challenge to tackle? Let’s face it. Together.
C-levels from these companies (AND MORE) relied on my expertise to overcome thEIR CHALLENGES IN THIS AREA. ANd You can, too.
Can I help you?Business Functions
• Zero-Based Redesign in support of marketing
A consumer packaged goods company launched a ZBR-based marketing program with the goal of redirecting revenue from marketing and sales categories to support new growth initiatives. First, the team created a database with more than fifty cost categories across all business units. Then it applied industry qualitative benchmarks to set goals for each category. Using the detailed information derived, the team identified some ways to save costs: for example, removing some components from the PR agency contract (reducing its overall fees) and cutting packaging costs. The company derived a 15 percent increase in spending efficiency. In addition, the whole process helped instill a sense of ownership among the managers of the departments involved.
• Zero-Based Redesign in support of reorganization
Zero-Based Redesign allows companies to model from scratch the operation and composition of each department. It invites companies to abandon the “we’ve always done it this way” mentality. Executives need to be aware of what’s going on in their company, and redesign everything from there. But not only in times of fear or anxiety, even when things are going well. Companies must then break free from first-quartile benchmarks and retrospective analysis. This means thinking like digital natives, with an approach to the cost that “should be” for creating transformational savings rather than incremental reductions. The Zero-Based approach eliminates boundaries and places the right people to do the right work – a key solution to power profitable growth. But the talent ecosystem is fluid, composed of human labor, bots, virtual and cognitive agents, crowdsourcing, and of course, customers and suppliers.
Stay in wonderland
Let me show you how deep the rabbit hole goes.
Check out more of the Innovation Alphabet:

3D Printing
3D Printing
“3D printing” is a process carried out by an electronic device which, instead of resorting to the canonical ink, it molds almost any kind of material: from concrete to living tissue, most usually plastic, but also metal. And the operating principle is similar to that of a traditional printer. The creation of three-dimensional models can lead to the redesign of a company’s production capabilities.
Dive In
5G
5G
5G is the new frontier of cellular telephony. It was designed to improve (or completely replace) previous generations of mobile networks. The 5th generation features lower latency, ensuring flawless performance of business applications and many other digital experiences – thus enabling the new cultural generations to furiously play Fortnite away from home.
Dive In
Advanced Analytics
Advanced Analytics
The term “Advanced Analytics” refers to the ability to autonomously or semi-autonomously analyze data and content to identify correlations, develop analyses, predictions, and recommendations. It is not just a matter of collecting information and then organizing it into watertight compartments: the ultimate goal is to identify a dialogue pattern from a data-driven perspective.
Dive In
Agile
Agile
Agile is an approach to software development designed to respond to change. Teams quickly analyze the context in which they operate, identify uncertainties faced, and figure out how to adapt to always move forward. Interaction between individuals comes before processes and tools; collaboration with the customer is more important than negotiating contracts.
Dive In
Ansoff Matrix
Ansoff Matrix
The Ansoff Matrix is a marketing planning model that arises from the intersection of new and existing products and markets. It derives four possible strategies for expanding the company’s market, which are built around four variables with a changeable factor of risks and possibilities: existing product, new product, existing market, new market.
Dive In
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence is not strictly defined. Basically, it is a computer system able to make decisions in an independent and flexible way. A good AI application can perform everyday tasks better than an average person (e.g., identifying other people from their photos on social media or beating the best chess player). Nothing to fear, then. Unless you are a chess champion.
Dive In
Artificial Scarcity
Artificial Scarcity
We often tend to desire what we cannot have. Or what we are in danger of losing: Artificial Scarcity is a strategy that flaunts a limited number of items that do not correspond to actual availability. The goal is to stimulate the perception in consumers that the stock of items is about to run out and thus create a need based on the “fear of being cut off” or the intention to buy the item in order to resell it at a higher price.
Dive In
Attack Surface
Attack Surface
The term attack surface refers to the part of a system that may be subject to attack or breach by hackers. The smaller that surface is, the easier it will be to protect it. Indeed, the Internet is an ocean of deep, dark waters: those who navigate it must be aware that they are exposing themselves to a flood of digital risks. Yet, ironically, we do not need a big boat to shelter us.
Dive In
Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality is an ever-evolving technology that overlays multimedia information on top of our common sensory horizon to gain a deeper understanding of our surroundings. No, it doesn’t allow you to step out of the Matrix dream simulation, nor can it be accessed by swallowing a red pill. But neither is it the disturbing experience of the Playtest episode of Black Mirror.
Dive In
Balanced Scorecard
Balanced Scorecard
In business, as in life, you need balance. The Balanced Scorecard is a holistic tool for strategic management. It offers, in fact, the possibility of assessing corporate performance in its wholeness. An overview that embraces four perspectives: the business/financial side, customers and stakeholders, internal processes, and learning and growth.
Dive In